Part I: Understanding Your Body and the Transformation Process
Chapter 1: How Does Your Body Work?
The Basic Physiology of Weight Loss and Muscle Gain

Your body is a remarkable system, constantly adapting to what you eat, how you move, and even how you think. When you aim for weight loss or muscle gain, two fundamental processes come into play: catabolism (breaking down) and anabolism (building up).
Weight loss occurs when your body is in a caloric deficit—burning more calories than it consumes. Muscle gain requires a caloric surplus, paired with sufficient protein and resistance training.
The Role of Hormones in Weight Regulation
Hormones like insulin, cortisol, leptin, and ghrelin are the key players in weight management. Insulin, for instance, helps regulate blood sugar levels and fat storage. Excess insulin due to high sugar intake can promote fat storage. Conversely, reducing sugar and improving insulin sensitivity through a balanced diet and exercise can aid fat loss.
Scientific Example: A study published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism showed that a low-carb diet improved insulin sensitivity in overweight individuals, resulting in significant fat loss over six months.
Chapter 2: Setting Realistic Goals and Measuring Progress

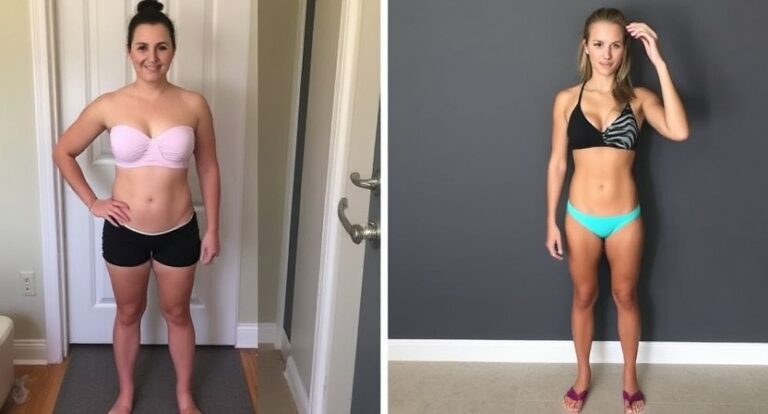
Setting realistic goals for fat loss is crucial for long-term success and maintaining a healthy mindset. Instead of aiming for drastic weight loss that can be both physically and mentally taxing, consider adopting a more gradual approach. Establishing a goal to lose about 1 to 2 pounds per week is often a sustainable and achievable target. This not only helps prevent the frustration that comes with unrealistic expectations but also minimizes the risk of losing muscle mass, which is essential for a healthy metabolism.
When setting your goals, it is beneficial to focus on specific metrics beyond just the number on the scale. Consider incorporating body measurements or body composition percentages to get a fuller picture of your progress. You could aim to reduce your waist circumference by a couple of inches or to increase your muscle mass over time. By expanding your focus beyond weight alone, you can celebrate improvements that happen with muscle tone, energy levels, and overall health.
To measure progress effectively, it’s important to monitor your journey regularly but without obsessing over daily fluctuations. Tracking your weight weekly, alongside body measurements and even photographs, offers a more comprehensive view of your advancements. Logging your food intake and exercise routine can help identify patterns and keep you accountable while also encouraging healthier choices.
Don’t forget to honor your non-scale victories, such as increased stamina during workouts, improved mood, or feeling more comfortable in your clothing. These qualitative measurements can be incredibly motivating and help maintain your commitment to your goals.
Setting SMART Goals
Your goals should be:
- Specific: “Lose 5 kg of body fat.”
- Measurable: “Reduce body fat percentage from 30% to 25%.”
- Achievable: “Walk 10,000 steps daily for three months.”
- Relevant: “Improve health and confidence.”
- Time-bound: “Achieve this by June 1st.”
Tracking Progress Effectively
Progress isn’t just about the scale. Use tools like:
- Weight tracking: Weekly measurements.
- Body fat percentage: Using calipers or smart scales.
- Strength benchmarks: Tracking gym performance.
- Visual changes: Progress photos taken monthly.
Real-life Story: Sarah, a mother of two, set a SMART goal to lose 10 kg in six months by tracking her meals, increasing her protein intake, and committing to 30-minute strength workouts thrice a week. She lost 12 kg and reduced her waist circumference by 10 cm, proving the power of clear, actionable goals.
Part II: Nutrition for a Healthy Body
Chapter 3: Building a Balanced Diet

Creating a balanced diet is a crucial component of any fat loss journey. It’s important to approach this goal with a mindset focused on nourishment and sustainability rather than restriction and deprivation. A well-rounded diet not only supports fat loss but also fosters overall well-being, energy, and vitality.
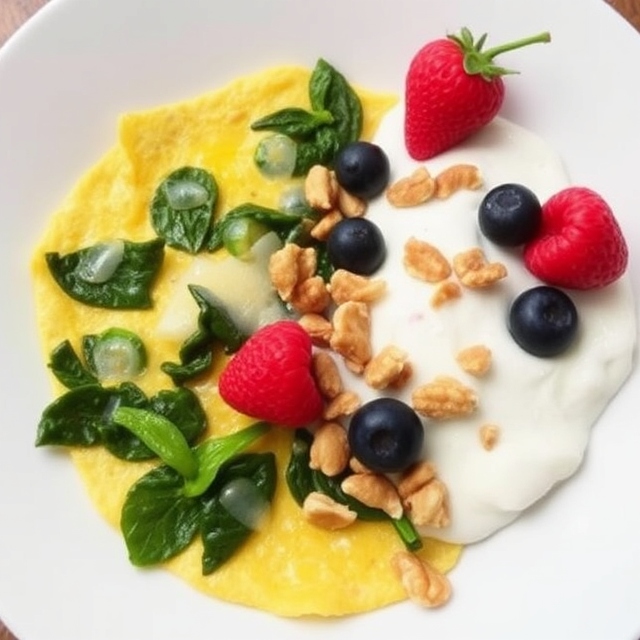
Imagine starting your day with a breakfast that fuels your body and mind. Incorporating whole grains, such as oats or whole-grain bread, can provide slow-digesting carbohydrates that keep you satiated throughout the morning. Pairing these with a source of protein, like Greek yogurt or eggs, gives you the balanced start to your day that enhances muscle preservation while you’re in a calorie deficit. Don’t forget to add in some fruit or a handful of nuts for healthy fats, fiber, and that extra boost of vitamins.
As you approach lunch, think about building a colorful plate. Fill half your plate with a variety of vegetables—leafy greens, bell peppers, and carrots—not only for their low-calorie content but also for their wealth of nutrients. Choose a lean protein source, such as grilled chicken, tofu, or legumes, to help maintain muscle mass and promote recovery. Whole grains or healthy fats, like quinoa or avocado, can serve as powerful additions, providing sustained energy and promoting feelings of fullness.
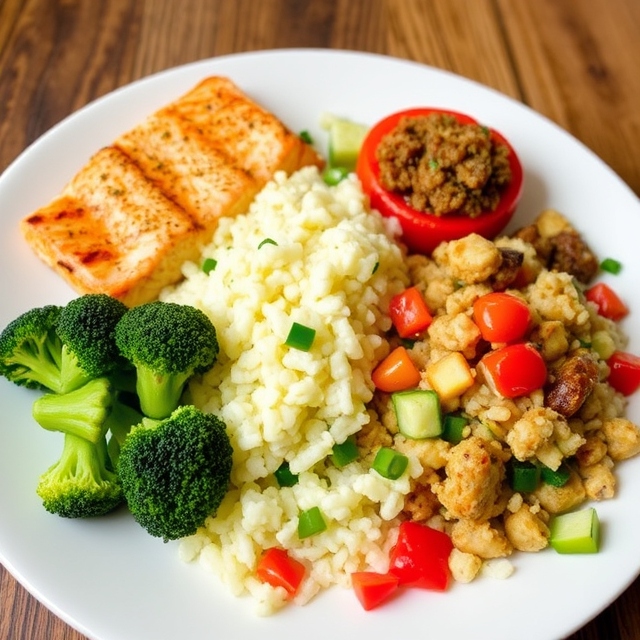
Dinner can be another opportunity to reinforce your commitment to a balanced diet. Consider it a chance to experiment with different cooking methods and flavors. Roasting or grilling vegetables can enhance their natural sweetness and texture, while incorporating a healthy source of fat, such as olive oil or nuts, can elevate the taste. Again, lean protein should take center stage, ensuring you’re not just focusing on calories but also on the quality of the foods you’re consuming.
Snacking can often derail progress, but it doesn’t have to. Instead of processed options, keep wholesome snacks at hand, such as sliced veggies with hummus, Greek yogurt with berries, or a small handful of nuts. These snacks provide a satisfying crunch or creaminess while keeping your energy levels stable and hunger at bay.
Hydration plays an equally important role in a balanced diet for fat loss. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can aid digestion, reduce cravings, and enhance your overall sense of well-being. Sometimes, our bodies mistake thirst for hunger, leading us to consume extra calories when all we really need is a glass of water.
The Essential Food Groups
A balanced diet should include:
- Proteins: Essential for muscle repair. Examples: chicken, eggs, lentils.
- Carbohydrates: Your body’s primary energy source. Choose whole grains over refined carbs.
- Fats: Necessary for hormone production. Prioritize healthy fats like avocados and nuts.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Found in colorful fruits and vegetables.
Meal Example: A balanced lunch might include grilled chicken breast, quinoa, steamed broccoli, and an orange.
Chapter 4: Portion Control

Portion control is a fundamental aspect of any successful fat loss strategy. Understanding and managing portion sizes can significantly impact your calorie intake and overall diet quality, leading to more effective weight management.
When we think about portion control, it’s essential to recognize that it’s not merely about eating less; it’s about being mindful of what and how much we are consuming. One of the most powerful tools in this regard is awareness. Often, we eat mindlessly while distracted by television, smartphones, or other activities, leading to overeating. By practicing mindful eating, we can reconnect with our body’s hunger cues and recognize when we’re satisfied, allowing us to enjoy our food without excess.
Visual cues can also aid in portion control. Many people find that using smaller plates or bowls helps to reduce portion sizes without feeling deprived. This simple trick leverages the psychology of perception—smaller dishes make portions appear larger, fulfilling our visual expectations and encouraging satisfaction with less food.
Additionally, understanding serving sizes, particularly for high-calorie items, can drastically shift our eating habits. Through education about what constitutes a single serving, we become empowered to measure our intake more accurately. For instance, when it comes to nuts, which are calorie-dense but packed with nutrients, a small handful can suffice when we are informed about appropriate serving sizes.
Another key component of portion control is planning and preparation. By taking the time to prepare meals in advance and portion them out appropriately, we can remove the guesswork when hunger strikes. This not only helps manage calorie intake but also promotes healthier options over convenience foods that are often higher in calories and lower in nutritional value.
It’s also important to listen to our bodies. Everyone’s metabolism and activity levels differ, so what works for one person might not work for another. Recognizing our individual needs allows us to adjust portions intelligently. Hunger and fullness cues are vital indicators; learning to honor them can help us establish a more intuitive relationship with food.
Understanding Caloric Needs
Your daily caloric intake depends on factors like age, weight, activity level, and goals. Use tools like the Harris-Benedict equation to estimate your needs.
Portion Management Techniques
- Calorie tracking apps: MyFitnessPal, Cronometer.
- Plate method: Fill half your plate with veggies, a quarter with protein, and a quarter with carbs.
Example: If you burn 2,000 calories daily and aim for fat loss, a 1,500-calorie intake could create a sustainable deficit.
Chapter 5: Nutritional Supplements

When it comes to fat loss, many people often turn to nutritional supplements in hopes of accelerating their progress. While there’s no magic pill that guarantees success, the right supplements can complement a balanced diet and regular exercise, helping to create a more effective weight loss strategy.
One of the most popular types of supplements for fat loss is the thermogenic fat burner. These formulations typically contain ingredients such as caffeine, green tea extract, and capsaicin, which can help increase metabolism and enhance fat oxidation. By boosting energy levels and promoting thermogenesis, thermogenic fat burners may provide the extra push some individuals need to tackle their workouts more fiercely and sustain their energy throughout the day.
Another category worth mentioning is appetite suppressants, which can aid in reducing cravings and controlling hunger. Ingredients like glucomannan, a fiber derived from the root of the konjac plant, can expand in the stomach, leading to a feeling of fullness. This can be particularly beneficial for those who struggle with portion control or late-night snacking. However, it is essential to remember that reliance on supplements should not replace the importance of healthy eating habits and mindful consumption.
Additionally, protein supplements can play a vital role in a fat loss plan. High protein intake not only supports muscle recovery and growth but also helps promote satiety. Whether in the form of whey protein, casein, or plant-based options, adding a protein supplement to your daily routine can help ensure you meet your nutritional needs while creating a feeling of fullness that can prevent overeating.
It’s also worthy to mention the role of omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil supplements. Not only are they beneficial for overall health, including heart and brain function, but they may also contribute to fat loss by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation. By supporting metabolic health, omega-3s can indirectly assist with maintaining a healthy weight.
While nutritional supplements can be supportive tools in your fat loss journey, they are most effective when integrated into a well-rounded lifestyle. It’s critical to remember that no supplement can replace the foundational elements of weight loss: a balanced diet rich in whole foods, regular physical activity, and adequate rest and recovery.
When Are Supplements Needed?
Supplements fill gaps in your diet. For example:
- Vitamin D: For those with limited sun exposure.
- Protein whey: Helps meet protein goals post-workout.
Scientific Insight: A study in Sports Medicine found that individuals who consumed whey protein within 30 minutes of resistance training experienced more muscle growth than those who didn’t supplement.
Part III: Effective Exercise Strategies
Chapter 6: Choosing the Right Type of Exercise
When it comes to fat loss, choosing the right type of exercise can be a game changer in your fitness journey. It’s essential to understand that not all exercises yield the same results, and the effectiveness of a workout can vary based on individual preferences and body responses.
First and foremost, you should consider incorporating strength training into your regimen. This type of exercise builds muscle, and it’s a well-known fact that muscle burns more calories at rest compared to fat. By enhancing your muscle mass, you can boost your resting metabolic rate, allowing you to burn more calories throughout the day. Aiming for several sessions a week with exercises that target major muscle groups can profoundly impact your body composition over time.
Cardio exercises, on the other hand, can be effective for burning calories, especially when performed at higher intensities. Activities like running, cycling, or swimming get your heart rate up, engaging various muscle groups while promoting endurance. Incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) into your cardio routines can yield impressive fat loss results in shorter workout times. This method alternates between intense bursts of activity and brief recovery periods, maximizing calorie burn both during and after the workout.
But sustainable fat loss isn’t just about the calories burned during exercise; it’s equally about finding activities you enjoy. If you dislike running, forcing yourself to do it may lead to burnout and inconsistency. Opt for exercises that you find engaging—whether it’s dancing, martial arts, or group classes. When you enjoy what you do, you are more likely to stick with it, leading to better long-term results.
It’s also crucial to take into account the role of flexibility and recovery in your exercise regimen. Incorporating activities such as yoga or Pilates can support your overall fitness by improving muscle recovery, enhancing flexibility, and reducing the risk of injury. These practices can complement your strength training and cardio workouts, allowing you to maintain a balanced approach.
The best type of exercise for fat loss is one that harmonizes with your lifestyle, goals, and personal preferences. It’s not merely about hours spent working out but rather the consistency and enjoyment of the activities you choose.
6.1 Cardio
- Low-intensity: Walking, cycling.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Sprint intervals.
6.2 Strength Training
- Free weights: Dumbbells and barbells.
- Key exercises: Squats, deadlifts, and bench presses.
6.3 Flexibility
- Yoga or Pilates to improve joint mobility.
Example Program: A weekly mix of three strength sessions, two cardio days, and one yoga session balances fitness.
Chapter 7: Proper Training Techniques
When it comes to effective fat loss, proper training techniques play a crucial role in maximizing your results and ensuring sustainable progress. Understanding the principles of training and how they apply to fat loss can make all the difference in your fitness journey.
One of the primary techniques for fat loss is incorporating a combination of both cardiovascular and resistance training. Cardiovascular exercises, such as running, cycling, or swimming, elevate your heart rate and help burn calories during the workout. However, resistance training is equally important, as it builds muscle mass, which in turn increases your resting metabolic rate. This means that the more muscle you have, the more calories you burn at rest, aiding in your fat loss efforts over time.
Another key technique is the concept of high-intensity interval training (HIIT). This training style alternates short bursts of intense activity with brief recovery periods, allowing you to maximize calorie burn in a shorter amount of time. HIIT not only boosts your metabolism during the session but can also lead to an increased metabolic rate even hours after the workout is done, known as the afterburn effect.
Consistency is a vital component of successful fat loss training. It’s important to establish a routine that fits into your lifestyle, ensuring that you can maintain your workouts over the long term. Setting realistic goals and being patient with yourself is paramount, as sustainable fat loss takes time and commitment. It’s also beneficial to mix up your workout routine to prevent plateaus and keep your body challenged, which further encourages fat loss.
Proper nutrition cannot be overlooked in conjunction with your training techniques. While exercise is key to burning calories, what you fuel your body with plays an equally significant role. Prioritizing a balanced diet rich in whole foods—lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables—will provide your body with the nutrients it needs to support your training. Additionally, paying attention to portion sizes and understanding your caloric needs will help create the calorie deficit necessary for fat loss.
Recovery is an integral part of any training program aimed at fat loss. Allowing your body adequate time to recover prevents injury and ensures that you are physically and mentally prepared for your next workout.
Learning correct form prevents injury and maximizes results.
Example: To squat correctly:
- Keep your chest up.
- Engage your core.
- Push through your heels.
Chapter 8: Boosting Motivation and Building Habits
Embarking on a fat loss journey is as much about cultivating a mindset and establishing lasting habits as it is about the physical changes we seek. Motivation can sometimes feel like a fleeting spark, easily extinguished by daily challenges and setbacks. However, by shifting our perspective and focusing on the intrinsic benefits of our goals, we can maintain a consistent drive.
Understanding that motivation often ebbs and flows helps us navigate our path with resilience. Rather than relying solely on moments of inspiration, it’s crucial to anchor ourselves in a deeper purpose. Whether it’s the desire for improved health, increased energy, or enhanced self-confidence, identifying these core motivations will provide a steady foundation to return to on tougher days.
Building lasting habits is another essential component of this journey. It’s not just about short-term dietary changes or sporadic workouts; successful fat loss is rooted in consistent behaviors that eventually become second nature. To create these habits, we must cultivate an environment conducive to our goals. This means surrounding ourselves with supportive individuals, setting up our living space to encourage healthy choices, and being mindful of our triggers and temptations.
Start small. Rather than attempting a complete overhaul of our lifestyle overnight, focus on introducing manageable changes that can be gradually built upon. This could be as simple as incorporating an additional serving of vegetables into a meal or committing to a daily 10-minute walk. As these small actions lead to early successes, they can significantly boost our motivation and create momentum.
Additionally, tracking progress can become a potent tool in this process. Maintaining a journal or using apps to monitor food intake, workouts, and even mood shifts can help in identifying patterns and celebrating milestones. These small victories are vital; they reinforce our commitment to the journey ahead and provide tangible proof of our efforts.
Moreover, embracing a mindset of self-compassion is crucial. Understand that setbacks are part of the process; they don’t define our journey or diminish our efforts. Instead of viewing a slip-up as a failure, see it as an opportunity to learn and recalibrate. This approach fosters resilience, allowing us to bounce back more robustly than before.
As we venture forward, remember that this journey is not merely about reducing numbers on a scale but about embracing a healthier, more fulfilling lifestyle. By nurturing our motivation, fostering positive habits, and maintaining a compassionate perspective toward ourselves, we can create a sustainable path toward fat loss and overall well-being. Each step we take, no matter how small, brings us closer to our goals and a more vibrant version of ourselves.
Find intrinsic motivation (better health) and extrinsic motivation (an accountability partner).
Story: John, a desk worker, partnered with a friend for gym sessions. The camaraderie kept him consistent, leading to a 15 kg weight loss in a year.
Part IV: Mental Health and a Healthy Lifestyle
Chapter 9: The Role of Sleep
Sleep plays a pivotal yet often underappreciated role in the process of fat loss. When we think about shedding pounds, our minds frequently zoom in on diet and exercise, but the significance of quality sleep cannot be overstated. Sleep is not merely a passive state; it is a critical period for recovery, hormone regulation, and metabolic function.
During sleep, the body undergoes numerous restorative processes. Hormones that regulate appetite, such as ghrelin and leptin, are impacted by the amount and quality of sleep we get. Ghrelin, which stimulates hunger, tends to increase when we are sleep-deprived, leading us to crave high-calorie foods. Conversely, leptin, which signals satiety, decreases, leaving us less satisfied after meals. This hormonal imbalance can foster unhealthy eating patterns, making it challenging to adhere to a fat loss regimen.
Moreover, lack of sleep can affect our energy levels and motivation for physical activity. When we’re tired, our brains lean towards convenience rather than making choices that align with our fitness goals. This could mean reaching for quick snacks rather than preparing a healthy meal or skipping that workout in favor of restful inactivity.
Sleep also influences our body’s ability to recover from exercise. During deep sleep, growth hormone is released, which plays a vital role in muscle recovery and regeneration. Well-rested muscles are more efficient at burning fat, as a healthier body composition relies on a delicate balance of muscle and fat. To further compound the issue, insufficient sleep can lead to increased levels of cortisol, the stress hormone. Elevated cortisol levels can trigger cravings for unhealthy, sugary foods and encourage the body to store fat, particularly around the abdominal area.
Additionally, adequate sleep enhances cognitive functions, ensuring that we make better choices throughout the day. We become more mentally equipped to plan meals, resist junk food temptations, and stay committed to a workout regimen.
In a world that often glorifies hustle and relentless productivity, it’s crucial to recognize that prioritizing sleep is a legitimate strategy for achieving fat loss. Establishing healthy sleep habits can create a strong foundation for not just weight management but overall well-being. By ensuring we get the rest we need, we give ourselves a better chance to succeed on our journey toward a healthier lifestyle. Ultimately, the connection between sleep and fat loss highlights the necessity of a holistic approach to health—one that encompasses not just what we eat and how we move, but also how well we rest.
Quality sleep reduces hunger hormones (ghrelin) and boosts fat-burning hormones (leptin).
Tips:
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Avoid screens before bedtime.
Chapter 10: Managing Stress
Chronic stress raises cortisol levels, leading to fat gain.
Stress-Reduction Techniques:
- Practice mindfulness meditation.
- Engage in stress-relief hobbies.
Managing stress is a critical component of any successful fat loss journey. Stress can significantly impact our physical and mental health, leading to behaviors that hinder our progress, such as emotional eating or decreased motivation to exercise. When we experience stress, our bodies produce cortisol, a hormone that, in elevated levels, can encourage fat accumulation, particularly in the abdominal area. Therefore, addressing stress is not just beneficial for our overall well-being; it’s essential for effective fat loss.
To manage stress effectively, it’s important to first become aware of its sources. Many people encounter stress from various aspects of life—work, relationships, or even the pressure to maintain a certain body image. Identifying these stressors allows us to develop strategies tailored to our specific needs. For instance, if work-related pressures are a major source of stress, incorporating mindfulness or meditation practices can help center your thoughts and provide clarity amidst chaos.
Engaging in regular physical activity is another powerful method of stress management that also plays a crucial role in fat loss. Exercise releases endorphins, the body’s natural mood lifters, which can reduce feelings of anxiety and improve overall mental health. Finding activities that you enjoy can make this a sustainable part of your routine, turning exercise into an enjoyable outlet rather than a chore.
Additionally, nurturing a balanced diet can have a profound impact on both stress levels and fat loss efforts. Foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins can help regulate mood and energy levels. By prioritizing whole, nutritious foods while minimizing processed items, you can support your body in managing stress more effectively and enhance your ability to maintain a caloric deficit, which is essential for fat loss.
Sleep also plays a vital role in stress management. Lack of sleep not only increases cortisol levels but can also lead to cravings for high-calorie, sugary foods, further sabotaging weight loss efforts. Establishing a sleep routine that prioritizes restful, quality sleep can aid in reducing stress and fostering a healthier lifestyle.
Chapter 11: Adopting a Holistic Lifestyle
Healthy habits like drinking 2-3 liters of water daily, avoiding sugary drinks, and nurturing social relationships contribute to long-term well-being.
Final Thought:
Transforming your body is a journey, not a sprint. Celebrate small wins, stay consistent, and enjoy the process. Let science and strategy guide you from flab to fit!
Adopting a holistic lifestyle for fat loss is not merely about calorie counting or following restrictive diets; it encompasses a comprehensive approach that nurtures the mind, body, and spirit. Imagine embarking on a journey where every aspect of your life harmoniously intertwines to support your goals.
Picture waking up each morning, greeted by the sun’s warm rays, as you begin with mindfulness practices that set a positive tone for your day. Engaging in meditation or gentle yoga can help center your mind, reducing stress and anxiety that often lead to emotional eating. This serene start fosters a deeper connection with your body, allowing you to listen to its signals more intuitively.
Nutrition plays a critical role in this holistic transformation. It’s about viewing food as nourishment rather than a means to an end. You begin to fill your plate with vibrant, whole foods, rich in nutrients, color, and flavor. Instead of focusing solely on fat loss, the emphasis shifts to overall health and vitality. You explore seasonal produce, savoring the natural flavors and discovering new recipes that excite your palate. This approach not only fuels your body but also enhances your relationship with food.
Physical activity evolves from a chore into a joyful expression. Whether it’s dancing, hiking, cycling, or participating in recreational sports, you find ways to move that resonate with your spirit. Regular exercise becomes an opportunity to celebrate your body’s capabilities rather than a punishment for what you eat. As you cultivate this joyful movement, you’ll find that your energy levels rise, further supporting your holistic wellness.
Social connections are another vital dimension of this lifestyle. Surrounding yourself with supportive individuals who share similar values nurtures a sense of community. Engaging in group activities, whether it’s cooking classes, group workouts, or sharing meals, fosters an environment of encouragement and accountability, keeping you motivated on your journey.
Moreover, embracing quality sleep and rest is essential. Recognizing the importance of restorative practices such as adequate sleep, self-care rituals, and relaxation techniques, helps to balance hormones that regulate hunger and stress. By prioritizing your well-being in this way, you create a solid foundation that supports consistent fat loss.